Seborrheic Dermatitis vs. Regular Dandruff: What’s the Difference and How to Manage Them

Few things feel as uncomfortable, or as noticeable, as flakes landing on your freshly pressed shirt. Beyond the visible distraction, persistent flaking can affect your confidence as well..
However, the flaking can be caused by various skin conditions, dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis being two of the most common ones. People unfamiliar with these conditions often get confused about the subject of “seborrheic dermatitis vs dandruff,” as both conditions lead to flakes and oiliness.
This article will help clarify all your confusions about both conditions and address those who ask if seborrheic dermatitis is the same as dandruff.
What Might Be Causing the Flakes?
Flakes can be confusing. Multiple conditions can lead to the formation of flakes and patches on the skin. So, is it dandruff or something else? It could be:
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Eczema
- Dry Skin
- Psoriasis
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that develops red, itchy rash-like patches on the skin along with flaking. Psoriasis also results in scales and plaques on the skin, but they are often silver in color and larger.
However, the symptoms of seborrhea and dandruff are different. Read on to learn more about them.
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic Dermatitis (SD) or Seborrhea is an inflammatory skin condition that results in the formation of oily flakes and scaly patches on the skin. Some other common symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are:
- Itching
- Yellow or white thick flakes
- Redness on the skin
- Irritation
The flaking usually appears on the scalp, beard, and eyebrows. However, the symptoms can appear anywhere on the body. The redness is more common in areas where sebaceous glands are more active, such as
- Behind the ears
- Around the nose and mouth
- Chest
- Back
- In the skin folds.
It is believed to be caused by Malassezia yeast, which normally lives on the skin. The symptoms may sound intimidating, but the good news is that this condition is not contagious.
What is Dandruff?
Dandruff, which most of us are familiar with or have dealt with at least once in our lives, is flakiness and oiliness on the scalp. It is believed to be caused by the same Malassezia yeast that leads to seborrheic dermatitis.
You can think of dandruff as the calmer sibling of seborrheic dermatitis. It results in the formation of oily and greasy flakes on the scalp that are very annoying. Almost half of the world’s population experiences dandruff at some point in their lives. Males are more prone to it.
The primary symptoms of dandruff are:
- Yellowish or white flakes
- Oiliness on the skin
- Greasy patches on the scalp
- Itching
The flakes caused by dandruff are more common on the scalp; however, they can also appear on the eyebrows, mustache, and when they appear on the beard, it is usually known as beard dandruff or beardruff.
What Causes Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis?
The causes of dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis are pretty much the same. They are caused by various factors such as
- Malassezia
It is a yeast that normally lives on everyone’s skin as part of the natural microbiome. Under certain conditions, however, this yeast can overgrow and contribute to seborrheic dermatitis.
- Overactive Sebaceous Glands
One key factor is sebum, the natural oil produced by sebaceous glands. When sebum production is high, it provides an abundant food source for Malassezia that helps it to grow at a much faster rate.
- Reaction to Oleic Acid
As the yeast metabolizes sebum, it breaks down triglycerides and releases byproducts such as oleic acid. In people who are sensitive to these byproducts, this can disrupt the skin barrier, accelerate the turnover of skin cells, and trigger local inflammation. The result is a combination of flaking, redness, itching, and irritation.
Ultimately, it is not simply sebum or Malassezia alone, but the interaction between excess sebum, Malassezia overgrowth, and the body’s inflammatory response that leads to the visible symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff.
Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Dandruff: Key Differences
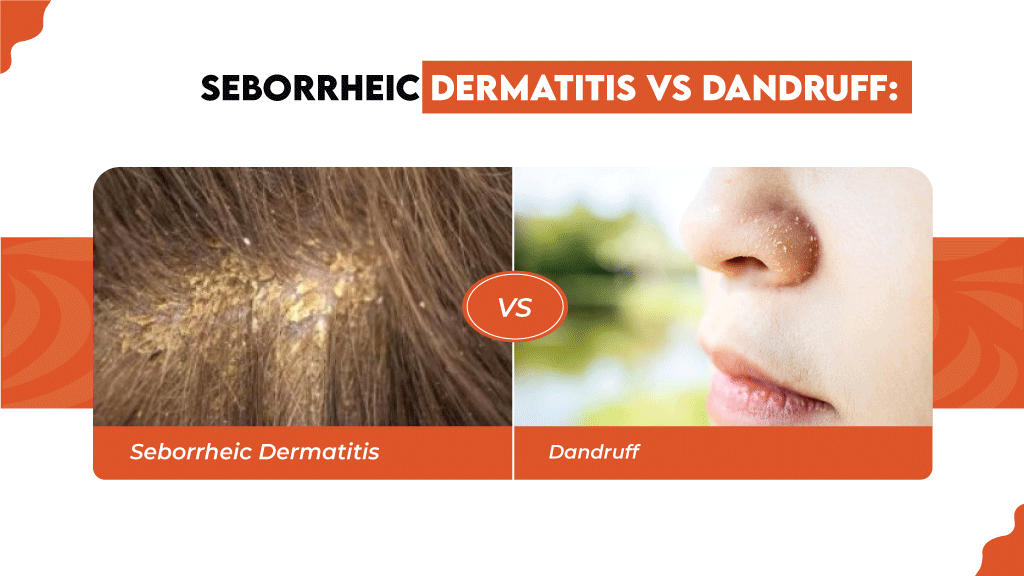
How do you know if you have seborrheic dermatitis or dandruff? Dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis may be caused by the same yeast and look quite similar; however, there are a few differences between them.
Here are some of the key differences to help you tell them apart.
| Dandruff | Seborrheic Dermatitis | |
| Appearance of flakes | White or yellow thin flakes that can be dry or a little oily | White or yellow flakes that are thick and greasy |
| Severity | Mild | More severe |
| Location | Mostly on the scalp, but can also appear on the beard and eyebrows | Scalp, beard, eyebrows, |
| Redness | Usually does not cause redness | Can lead to redness around the nose, behind the ears, under the beard, chest, and back |
| Inflammation | No | Yes |
| Treatment | Anti-dandruff shampoo | OTC medicated shampoo |
What Triggers Flakes on the Scalp and Face?

We know that dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis can cause flakes. However, certain factors have been shown to contribute to flakiness and can make the condition worse.
These are:
Environmental Factors
The environment you live in can contribute to improving or worsening the condition. That is why flakes often appear in dry and harsh environments. When the skin becomes dry and sensitive, it becomes more prone to skin issues. A hot environment can create a favorable environment for yeast to thrive, leading to seborrheic dermatitis on the body, which can result in a flaky and itchy beard, scalp, and face.
Skin Sensitivity
People with a sensitive skin barrier may be more prone to conditions like dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. A compromised or thinner barrier makes it easier for irritants and microorganisms to trigger inflammation.
In seborrheic dermatitis, the skin often shows an exaggerated immune response to byproducts of Malassezia yeast. Instead of tolerating this common skin organism, sensitive skin may overreact, leading to increased redness, itching, and flaking.
This explains why some individuals experience recurrent flare-ups while others with the same yeast levels do not.
It’s not that the skin is “attacked” by infections, but rather that an overactive inflammatory response combined with barrier vulnerability contributes to persistent symptoms of dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, as previously described, can lead to the formation of flakes. Eczema is the opposite of oily. It can result in patches of itchy and flaky skin. The same goes for psoriasis. However, psoriasis is more flaky and scaly than eczema. If you have an underlying skin condition, treat it first and then address the flakes.
Genetics
Even though there is not much research done on it, some researchers believe that seborrheic dermatitis can be triggered due to genetics. How? Certain gene mutations can trigger the sebaceous glands to produce excess sebum that can lead to inflammation and flaking.
Using Wrong Products
If you use products that are harsh on your skin, an allergic reaction could result in flakes and potentially harm your skin and hair. Additionally, doctors may recommend avoiding the use of certain beauty products when dealing with SD.
How to Get Rid of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Regular Cleansing
Keeping the affected area clean with a medicated shampoo or wash can help you reduce the symptoms and treat the root cause of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff.
- For regular dandruff, using an anti-dandruff shampoo at least 2 to 3 times a week can help reduce the flaking and scaling.
- However, for seborrheic dermatitis, you may need to use a stronger medicated wash that contains active ingredients like pyrithione zinc daily to wash the affected area, especially when the scaling and flaking are severe.
Dandruff Comb or Brush
If you are eager to get rid of the flaking fast, then you can use a fine-toothed dandruff brush or comb to gently brush your hair while shampooing to get rid of the excess loose flakes.
Practicing Good Hygiene
Hygiene can worsen or improve your symptoms. Good hygiene includes:
- Trimming your hair regularly
- Exfoliating your skin occasionally
- Following a consistent bathing routine
- Using a gentle fragrance-free shampoo on your hair
- Moisturising your skin
Don’t Scratch or Pick at Flakes
The itching associated with dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis can be very irritating and hard to resist. However, scratching the affected area or picking at flakes can damage the skin and hair follicles and lead to other complications such as hair loss and skin infection.
Can Shaving Help with Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis?
There’s a common myth that shaving your head or beard will get rid of dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis. In reality, shaving may temporarily remove visible flakes, but it does not address the root causes of the condition.
Inflammation, redness, itching, and irritation can persist even on freshly shaved skin. Effective management requires the right treatment, which should include a medicated anti-dandruff shampoo rather than simply removing the hair.
Medicated Wash for Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff
There are a lot of products labeled as anti-seborrheic dermatitis or anti-dandruff solutions. But it may be difficult to pick just one. So, which solution will be good for managing associated symptoms with both conditions, no matter how severe they are? Well, the 3-in-1 wash by Facial Fortress should be your choice. And there are several reasons to choose this. It:
- Reduces itching, redness, and irritation associated with SD and dandruff
- Good for all skin types
- Can be used on the face, scalp, and beard
- Contains extracts from nature
- Does not contain harsh chemicals
- Does not contain fragrance or ingredients that mask fragrance.
- Made specially for individuals with sensitive skin
- Soften the beard
- Created by a doctor
It is developed by Dr Eddie, a board-certified pediatrician who is also the founder of Happy Cappy Shampoo, the first brand to develop OTC cradle cap shampoo.
Whether the flakes are on your scalp, face, beard, or other areas, Dr. Eddie’s 3-in-1 Medicated Wash can help you reduce them. It contains 0.95% zinc pyrithione as an active ingredient that has been known to be effective by various studies in controlling the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin.
With daily use, many people notice visible improvement within just a few washes.
How to Prevent Both Conditions?
Even though you can not entirely prevent dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis, there are a few things that you can do to prevent future flaking or your condition from getting worse:
- Keep your scalp and skin clean. Take regular baths, but don’t overdo it.
- Use lukewarm water, as hot water can strip away natural oils.
- Regularly moisturize your skin.
- Avoid using natural oils.
- Avoid prolonged direct exposure to heat and sunlight.
- Do not pick flakes.
- Do not scratch the skin if it itches. Use medicated shampoo or apply a cold compress for relief.
Final Thoughts
The “dandruff vs seborrheic dermatitis” issue has hopefully been clarified now. Seborrheic dermatitis is a more inflammatory condition that causes scaly, flaky, and itchy skin and can appear on many areas of the body.
Dandruff, its milder form. Both conditions can be effectively managed with the regular use of medicated anti-dandruff shampoos.
- Daily Beard Care Myths That Could Be Making Flakes and Itch Worse - March 3, 2026
- Dry, Flaky Skin Under Your Mustache? Causes, Quick Fixes, and Beard Care Tips - February 13, 2026
- How Often Should I Wash My Hair and Beard to Control Dandruff? (Doctor Guide) - February 13, 2026
Recent Post
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between seborrheic dermatitis and regular dandruff?
Can stress make seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff worse?
Can diet affect seborrheic dermatitis?
When should I see a dermatologist?
If you see that:
- Symptoms are continuously worsening
- Symptoms not improving
- Skin has cracks and is bleeding
- There are signs of infection
- Patches are oozing
Then, you must consult a healthcare professional.
Can children or babies get seborrheic dermatitis?
- Daily Beard Care Myths That Could Be Making Flakes and Itch Worse - March 3, 2026
- Dry, Flaky Skin Under Your Mustache? Causes, Quick Fixes, and Beard Care Tips - February 13, 2026
- How Often Should I Wash My Hair and Beard to Control Dandruff? (Doctor Guide) - February 13, 2026





