Seborrheic Dermatitis And Hair Loss: How Gentle Scalp Care For Sensitive Skin Helps Prevent Thinning

If you are experiencing itchy, flaky, red scalp and hair thinning and loss, then you are not alone. Many men experience this frustrating combination without realizing the real culprit behind it: seborrheic dermatitis. Flaking and itching are common symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis, but can seborrhea cause hair loss?
Read this blog to discover whether seborrheic dermatitis causes hair thinning and how gentle scalp care can help prevent thinning.
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis, or SD, is a common inflammatory skin condition that causes a flaky scalp and beard. You can say it’s a more severe form of dandruff. Even though it is more common on the scalp, it can affect other parts of the body as well. Especially those that are rich in sebaceous glands, such as
- Eyebrows
- Sides of the nose
- Neck
- In the skin folds
- Beard area
While flaking on the hair is its prominent feature, it can also lead to some other common symptoms, such as:
- Itchy skin
- Redness on the skin
- Inflammation
- Yellow or white flakes
- Crusty scales
- Skin irritation
- Excessively oily or dry skin
It is believed to be caused by a combination of factors, like the presence of excess sebum on the skin, overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, and skin sensitivity towards oleic acid. These factors work together to give you those embarrassing flakes.
Does Seborrheic Dermatitis Cause Hair Loss?
Two of the most common questions that we often get are “Can seborrheic dermatitis lead to hair loss?” Or “Can dandruff cause hair loss?” The answer to both these questions is the same.
Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff can not directly cause hair loss. But it has a deep connection to hair loss and thinning. How? This can happen due to many different reasons, such as
- Due to the inflammation, hair follicles become irritated and less efficient, which disrupts healthy hair growth and causes hair thinning.
- Excess sebum on the skin and flakes can clog the pores and hair follicles, which makes it difficult for new hair to grow properly.
- Scratching the irritated scalp and skin can weaken or damage the hair follicles, which leads to hair loss.
Even though seborrheic dermatitis can cause temporary hair loss, the good news is that once the inflammation and condition get under control, the hair grows back. Seborrheic dermatitis hair loss recovery time is usually around a few weeks or months.
Seborrheic Dermatitis and Hair Loss Treatment
Hair thinning from seborrheic dermatitis is common, but the good news is, it’s manageable and often reversible. The most effective way to reduce shedding is to treat the underlying inflammation and flaking first. Once the scalp condition improves, healthy hair growth usually follows.
There are two main approaches to managing seborrheic dermatitis and related hair loss:
Use an Anti-Dandruff Shampoo
During flare-ups, dermatologists typically recommend using an anti-dandruff or anti-seborrheic shampoo daily to help reduce yeast buildup, soothe irritation, and control flaking. Once symptoms improve, you can reduce usage to 2–3 times per week for maintenance.
Look for shampoos that are:
- Fragrance-free, paraben-free, and sulfate-free
- Free from dyes, alcohols, and phthalates
- pH-balanced and gentle on sensitive skin
A great example is the Facial Fortress Anti-Dandruff Shampoo, formulated with 0.95% pyrithione zinc, a clinically proven ingredient that helps control dandruff, reduce flaking, and calm scalp irritation—all without harsh chemicals.
How to use it for the best results:
- Wet your scalp, beard, and hair with lukewarm or cool water (avoid hot water).
- Apply a small amount of shampoo and gently massage it into the scalp and affected areas.
- Let the product sit for 2–3 minutes to allow active ingredients to work.
- Rinse thoroughly, ensuring no residue remains.
Prescription Medications
For moderate to severe seborrheic dermatitis, your dermatologist may prescribe topical or oral treatments to control inflammation and yeast overgrowth. Common U.S.-approved options include:
- Topical antifungal agents
Ketoconazole 2%, Ciclopirox 1%, or Sertaconazole 2% creams/shampoos help reduce Malassezia yeast on the skin. - Topical corticosteroids
Hydrocortisone 2.5%, Desonide 0.05%, or Clobetasol 0.05% may be prescribed short-term to reduce redness, itching, and inflammation. - Topical calcineurin inhibitors (non-steroidal options)
Pimecrolimus 1% (Elidel®) or Tacrolimus 0.03–0.1% (Protopic®) may be recommended for sensitive areas, such as around the face or beard, to help control inflammation without steroid side effects. - Oral antifungals (for severe or widespread cases)
Fluconazole or Itraconazole may be prescribed in select cases to control persistent yeast overgrowth when topical therapy isn’t enough.
Note: These prescription options should be used only under medical supervision, as improper or prolonged use, especially of corticosteroids, can cause unwanted side effects.
By combining consistent, gentle scalp care with targeted medical treatment when needed, most people experience significant improvement in flaking, redness, and hair thinning caused by seborrheic dermatitis.
Gentle Scalp Care that Helps Prevent Thinning

Now that you know how to manage seborrheic dermatitis-related hair loss, let’s talk about prevention. With the right scalp care routine, you can help reduce inflammation, minimize flaking, and support stronger, healthier-looking hair before thinning even begins.
Here are a few dermatologist-recommended habits to keep your scalp balanced and resilient:
1. Avoid Scratching the Scalp
It’s tempting to scratch an itchy scalp, but doing so can injure the skin, inflame follicles, and worsen shedding. Constant scratching disrupts the protective barrier of the scalp, increasing irritation and prolonging flare-ups. Try instead to gently massage the area when applying medicated shampoo or a cool compress for relief.
2. Don’t Pick at Flakes
Those visible flakes can feel embarrassing, but picking or peeling them can backfire. Removing flakes forcefully may tear the skin, damage follicles, and in some cases, cause infection or scarring. A safer option is to use a medicated anti-dandruff shampoo and a soft scalp or cradle-cap brush to gently lift flakes while cleansing.
3. Choose the Right Hair and Beard Products
Many hair and grooming products contain fragrances, sulfates, parabens, and alcohol, which can strip the scalp of natural oils and trigger irritation or dryness. To help maintain scalp health and prevent thinning, opt for fragrance-free, paraben-free, and sulfate-free formulations.
A great example is the Facial Fortress 3-in-1 Face, Hair, and Beard Wash. It’s clinically tested, pH-balanced, and enriched with skin-hydrating ingredients such as glycerin, licorice root extract, and apple fruit extract, making it safe for sensitive or seborrheic-prone skin.
Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Cause Baldness?
Seborrheic dermatitis can sometimes cause temporary hair shedding, but it does not cause permanent baldness. When inflammation and irritation are brought under control, hair typically grows back.
If you’re noticing bald patches in addition to flaking or redness, it could indicate another condition such as tinea capitis (scalp ringworm) or alopecia areata. These could simultaneously occur with seborrheic dermatitis. In that case, consult a dermatologist for evaluation and targeted treatment.
Seborrheic Dermatitis and Alopecia: What’s the Connection?
The link between seborrheic dermatitis and alopecia is often misunderstood. Alopecia, particularly androgenetic alopecia (male-pattern hair loss), is a genetically driven condition that leads to gradual thinning and baldness over time.
When someone experiences both seborrheic dermatitis and alopecia, it may appear that SD is causing baldness. But in reality, the inflammation from seborrheic dermatitis only causes temporary shedding, while the true hair loss is due to alopecia.
The informal term “seborrheic alopecia” is sometimes used to describe shedding linked to severe or uncontrolled seborrheic dermatitis, but it is not a recognized medical diagnosis.
Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Cause Alopecia?
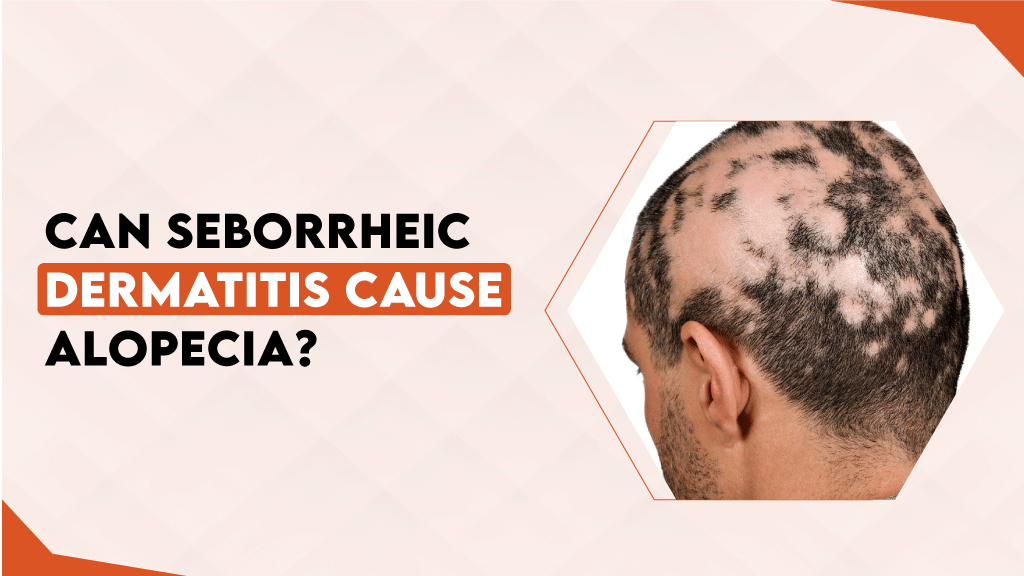
Simply put–no. Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast and an inflammatory response of the skin, while alopecia arises from genetic or autoimmune factors. Seborrheic dermatitis may lead to temporary hair loss, but once inflammation and scaling are managed, hair typically regrows.
Conclusion
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common scalp and skin condition that causes flaking, redness, and irritation on the scalp, beard, and other oil-rich areas of the body. Many people with seborrheic dermatitis notice temporary hair shedding or thinning, often mistaking it for permanent hair loss.
The truth is, seborrheic dermatitis itself does not directly cause baldness or permanent alopecia. However, inflammation, excess sebum, and scratching the scalp can weaken or irritate hair follicles, leading to temporary hair shedding.
The good news? Hair typically grows back once the condition is under control. With consistent and gentle care, you can support a healthy scalp environment and reduce the risk of hair thinning.
To care for your scalp and prevent further loss:
- Use a medicated anti-dandruff shampoo 2–3 times per week during flare-ups.
- Avoid scratching or picking at flakes, which can damage hair follicles.
- Choose gentle, fragrance-free products formulated for sensitive or seborrheic-prone skin.
- Follow a balanced diet and maintain hydration to support scalp health.
A mild, clinically tested cleanser like Facial Fortress 3-in-1 Medicated Shampoo, which contains 0.95% pyrithione zinc to help reduce flaking and irritation (associated with seborrheic dermatitis), can help maintain a balanced scalp and minimize hair thinning over time.
- Oily skin and beard dandruff: why over‑washing can make your beard flakier - December 23, 2025
- Why Your Beard Itches and Flakes: Seborrheic Dermatitis or Product Reaction? - December 23, 2025
- Seborrheic Dermatitis vs. Regular Dandruff: What’s the Difference and How to Manage Them - November 17, 2025
Recent Post
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I prevent hair loss from seborrheic dermatitis?
Can seborrheic dermatitis cause permanent hair loss?
Will my hair grow back after seborrheic dermatitis?
What is the best shampoo for seborrheic dermatitis and hair loss?
Look for a fragrance-free, paraben-free, sulfate-free shampoo containing active ingredients such as pyrithione zinc or ketoconazole.
The Facial Fortress 3-in-1 Medicated Shampoo includes 0.95% pyrithione zinc.
Can seborrheic dermatitis lead to baldness or alopecia?
How can I regrow hair after seborrheic dermatitis?
You can support regrowth by:
- Washing your scalp regularly with a gentle or medicated shampoo.
- Avoiding hot tools and harsh styling products.
- Eating a diet rich in vitamins A, D, E, biotin, and zinc.
- Avoiding aggressive scratching or exfoliating the scalp.
Hair generally regrows as the scalp’s barrier and microbiome return to balance.
- Oily skin and beard dandruff: why over‑washing can make your beard flakier - December 23, 2025
- Why Your Beard Itches and Flakes: Seborrheic Dermatitis or Product Reaction? - December 23, 2025
- Seborrheic Dermatitis vs. Regular Dandruff: What’s the Difference and How to Manage Them - November 17, 2025





